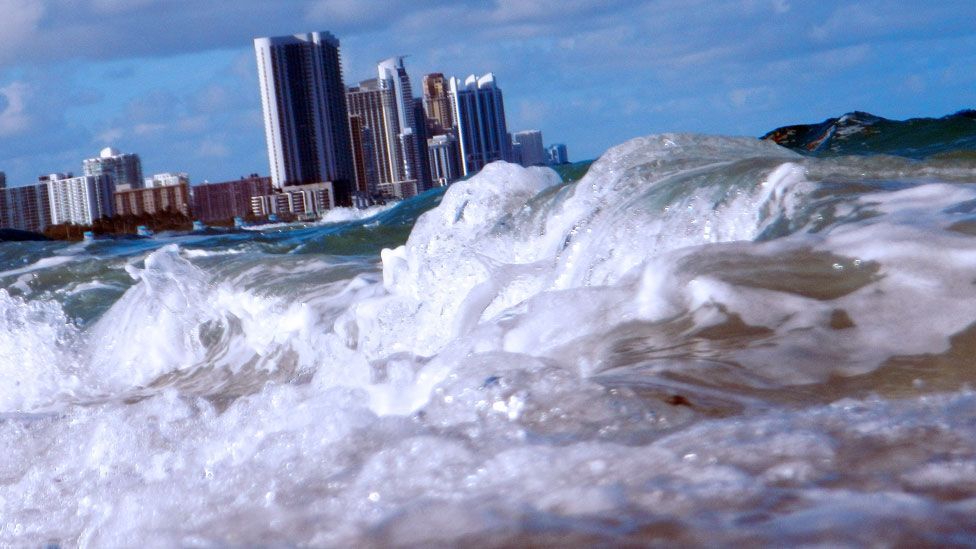
Coastal cities around the globe are facing unprecedented threats from rising sea levels, driven by climate change and melting polar ice caps. Urban areas in Asia, North America, and Europe report increasing flooding incidents, infrastructure damage, and population displacement.
Experts warn that without immediate action, millions of residents may face long-term disruption, with economic losses, health risks, and social instability becoming more severe.
Urban Impact and Infrastructure Risks
Flooding and storm surges compromise transportation, energy, and water systems in coastal regions. Airports, ports, and major highways are increasingly vulnerable, affecting commerce and daily life. Aging infrastructure struggles to withstand extreme weather events, highlighting the need for proactive urban planning and resilient design.
Water contamination, sewage overflows, and property damage exacerbate public health concerns. Emergency response systems are under pressure, and long-term mitigation strategies are urgently required to protect both residents and local economies.
Global Policy and Adaptation Measures
Governments and international organizations are prioritizing climate adaptation, investing in sea walls, flood barriers, and sustainable urban planning initiatives. Policy frameworks emphasize reducing greenhouse gas emissions, enforcing building codes, and incentivizing eco-friendly infrastructure.
Cities like Rotterdam, Tokyo, and Miami serve as models for integrated climate resilience, employing a combination of technology, urban design, and community engagement to mitigate the effects of rising waters.
Economic and Social Consequences
Rising sea levels have major economic implications, including property devaluation, insurance challenges, and disrupted trade. Coastal tourism and fisheries are particularly affected, impacting livelihoods and local economies. Social inequality is exacerbated, as vulnerable populations often lack resources to relocate or adapt.
Investments in green infrastructure and climate-resilient development not only reduce risks but also create employment opportunities, stimulate local economies, and promote sustainable growth.
The Role of Technology in Mitigation
Technological innovations, such as predictive modeling, smart flood monitoring systems, and climate-resilient construction materials, are critical in addressing rising sea levels. AI-driven risk assessments help policymakers prioritize interventions, while data analytics guide emergency response and urban planning.
Community engagement platforms enable citizens to report flooding incidents, track infrastructure performance, and participate in resilience-building initiatives, fostering collaborative approaches to climate challenges.
FAQs
What causes rising sea levels?
Melting ice caps, glacier retreat, and thermal expansion of oceans due to global warming contribute to rising sea levels.
Which cities are most at risk?
Coastal cities in Asia, North America, and Europe, particularly low-lying urban areas, are highly vulnerable.
How are governments responding?
Investments in sea walls, flood barriers, sustainable urban planning, and emission reduction initiatives are key measures.
What are the economic impacts?
Property damage, devaluation, disrupted trade, tourism losses, and challenges for fisheries significantly affect local economies.
How can technology help?
Predictive modeling, smart monitoring systems, AI-driven assessments, and resilient construction materials support mitigation and emergency response efforts.
Conclusion
Rising sea levels pose a severe threat to coastal cities, demanding urgent action from governments, communities, and international organizations. The combination of technological innovation, sustainable urban planning, and public engagement offers viable pathways to mitigate risk.
Proactive adaptation and resilience-building are essential to protect lives, preserve economies, and ensure sustainable growth. Addressing climate challenges today will safeguard future generations from the escalating impacts of a changing environment.